Studying Dentistry in Australia and New Zealand: A Complete Guide
Find out all you need to know about studying dentistry in ANZ, including different routes into dentistry, entry requirements, and tips for admission.

This article is written specifically for ANZ students.
Read the UK version here.
Dentistry has the power to transform lives.
That’s incredible in itself, but it’s also an in-demand profession with fantastic stability. The stumbling block for many is the high barrier to entry as university courses are extremely competitive and getting in takes total commitment.
Still interested? Read on to get a full breakdown of a career in dentistry.

Reasons to study dentistry
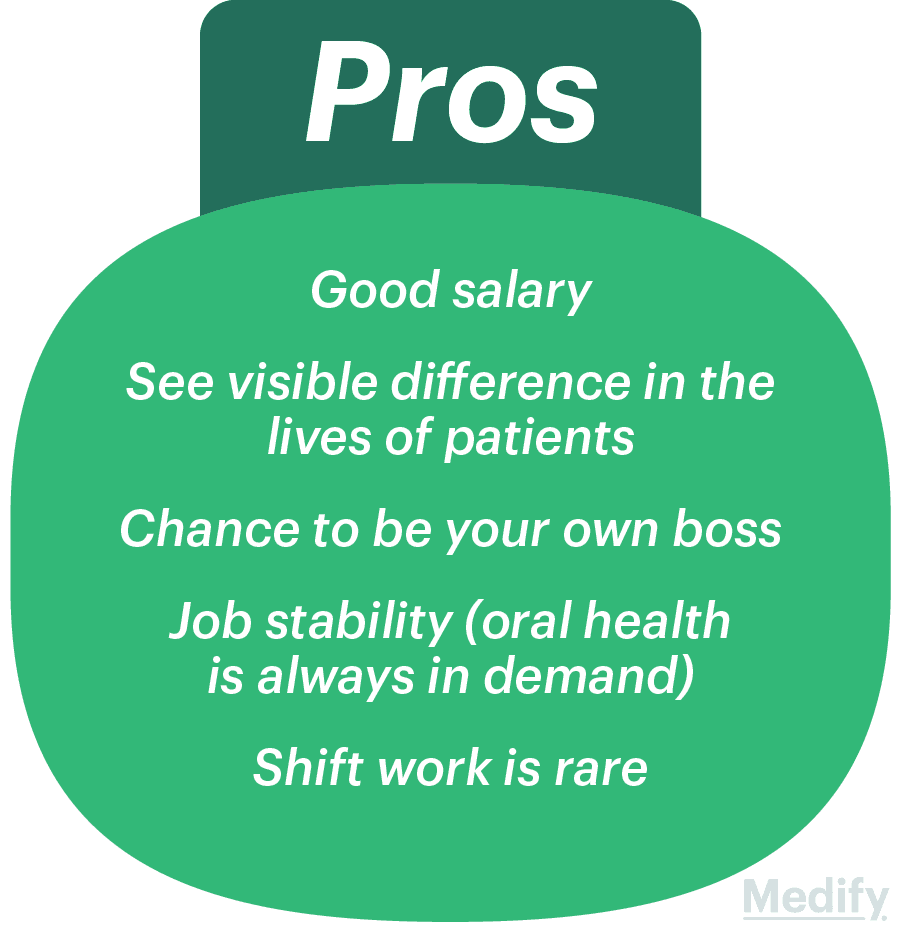

Is getting into dentistry competitive? What do I need and how can I improve my chances?
In short, yes. There are only 10 dental schools in Australia and New Zealand, with thousands of applicants eyeing a spot each year.
As a result, you need to think about your application holistically and prepare diligently to maximise your chances of success.
School grades
First, you will need strong academic credentials, such as an ATAR above 99 (for undergraduate courses) or a competitive GPA (for graduate courses). Prepare for your exams throughout the year to maintain high grades.
Admissions test
Second, you will need to perform well in an admissions test. Learn how these tests are run, find out the best resources to use, and start your preparation early.
If you’re applying as a school leaver or for undergraduate dentistry, it’s likely you’ll have to take the University Clinical Aptitude Test (UCAT ANZ). The UCAT ANZ is a two-hour, multiple choice, computer-based exam. It’s known for being extremely time pressured.
Improve your chances of succeeding in the UCAT by checking out the following resources:
Medify’s UCAT ANZ Online Course – 20,000+ questions, 25 unique full mock exams, 34 mini-mock exams, study notes and personalised performance feedback. You'll also get access to GAMSAT and Interviews courses.
If you’re applying as a graduate student, you may have to take the Graduate Medical Schools Admissions Test (GAMSAT). Find out more about the GAMSAT.
Interview
Third, most universities require an interview. Your interview will be in one of two formats:.
Semi-structured/panel
You’ll be interviewed by a panel of interviewers. Interviewers will ask you a series of questions and may also ask follow up questions. Semi-structured interviews have a less rigid format and are more likely to ask questions specific to you.
Multiple Mini Interview (MMI)
You’ll rotate around stations, and have a new interviewer and new interview question or task at each station. This format is much more structured as you’ll have a set amount of time at each station and all students will be asked the same questions.
Reflect on your motivations for dentistry, do readings around common dental topics and issues, and find out what dental school and dental career looks like.
Ask friends or family to help you out with mock interviews. This will help you become better at giving smooth and coherent answers. Interviews are always nerve racking so it’s important that you stay calm and make your answer relevant to the question.
Should I study dentistry or medicine?
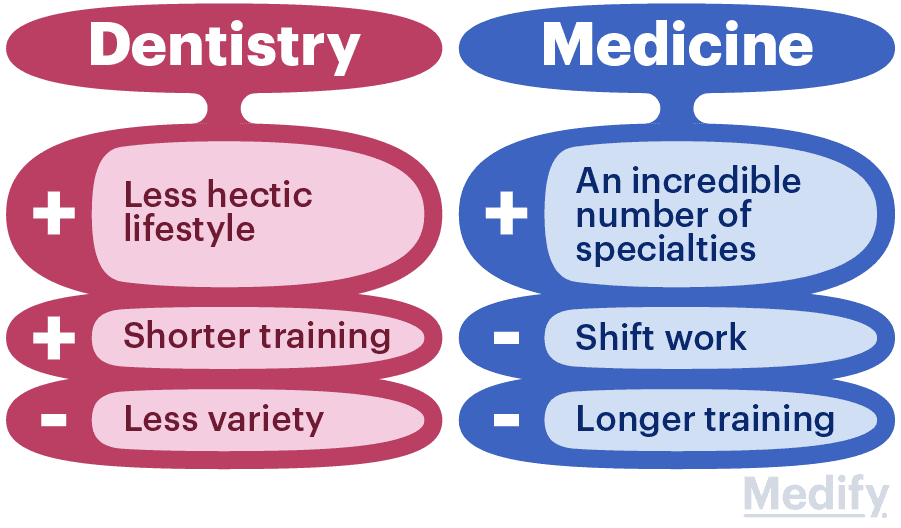
How long does it take to become a dentist?
Becoming a dentist can take five or more years depending on the path you choose. A standard 5-year undergraduate degree in dentistry will allow you to practise once you’ve graduated.
Graduate entry degrees are four years long, but you need to already hold at least a bachelor's degree to take this path. This means that doing a graduate entry pathway would take you at least seven years, and if you chose to do a masters or any other degree after your bachelor’s it can take even longer.
What are dental schools looking for?
The Australian Dental Association suggests that dentistry is an ideal career for people that enjoy specific activities. This means dental schools are looking for students skilled in those areas as they will most likely be able to become good dentists.
These skills include:
Excellent communication
Ability to interact with a range of people
Strong interpersonal skills
Ability to work both in a team and independently
Broad scientific and medical knowledge
Manual dexterity
Hand eye coordination
Great spatial awareness
Leadership
Business management interest
Which subjects do I need to study dentistry?
Although there may be slight variations in subject prerequisites, generally you’ll be required to study Chemistry, Biology and English.
Subjects that are often mentioned include:
Chemistry
Biology
English
Physics
Math
Do I need work experience?
Although work experience isn't compulsory, having work experience could give you an advantage at interviews. It’s likely that you may be asked some questions about your understanding of what a career in dentistry entails.
Work experience in a dental setting will enable you to show that you have a realistic understanding of what a doctor does. It’ll help you prove your point rather than make empty claims.
The golden question for interviews: ‘Why do you want to study dentistry?'
This question is central to most interviews. Dentistry is challenging but also rewarding so interviewers want to make sure you’re doing dentistry for the right reasons.
Here are the do’s and don’ts to acing this question:
| Do | Don't | | --- | --- | | Talk about personal experience: If you had a personal experience that led you to want to study dentistry, discuss it and reflect on it. | Use clichés: Avoid phrases like 'I’ve always wanted to be a dentist' or 'I really enjoy helping people'. This may be the case, but it’s what everyone says. | | Talk about your work experience: Mention something you saw in your work experience that spurred you on to pursue dentistry. | Talk about salary: It may be an incentive for you, but you don't want to come across as money-minded. | | Take a balanced approach: Discuss the positives and negatives of a career in dentistry (so you won’t sound naive). | Disrespect other professions: Interviewers may ask you why not a dental nurse or dental hygienist? Speak about all other professions with respect, as without them you wouldn’t be able to do your job. | | Back up what you say: If you’re going to say you enjoy hands-on jobs, tell the interviewer about a hobby of yours that requires hands-on skills. | Talk about family members in dentistry: This can influence your decision, but it’s important to focus on your own reflection rather than someone else's experience. |
What’s the deadline for dental applications?
Dental application deadlines vary based on where you’re applying to. Different TACs have different deadlines.
The deadline is usually around the end of September but make sure you check each TAC’s site for information on deadlines.
Dental universities: Where can I study?
Charles Sturt University
1800 275 278
Griffith University
1800 677 728
James Cook University
enquiries@jcu.edu.au
1800 246 446
La Trobe
1300 135 045
University of Adelaide
1800 061 459
University of Melbourne
1800 136 352
University of Queensland
dentistry@enquire.uq.edu.au
07 3365 8022
University of Sydney
1800 793 864
University of Western Australia
future-students@uwa.edu.au
(+61 8) 6488 3939
Average cost of studying dentistry
In Australia, dental degrees cost around $300,000 for full-fee paying students and $55,000 for commonwealth supported place (CSP) students. You’ll also need to pay for the UCAT ($325) and some tertiary application centres have a fee for submitting applications ($55-$210).
On top of that, if you’re moving away from home, you’ll have accommodation and living costs to pay for. Accommodation and living costs can vary based on where you’ll be studying. For example, accommodation and living costs tend to be more expensive in Sydney compared to Adelaide. You can use this handy calculator to work out how much your living costs and accommodation will be.
If you’re doing a 5-year dental degree, it could end up costing up to $440,000. In New Zealand, tuition fee for dentistry is $16,187 per year for years 2–5.
Is there an option to study dentistry part-time?
There are no universities that currently offer part-time dentistry. However, you can study some postgraduate courses part-time.
Can I study dentistry online?
Dentistry requires a lot of patient contact. You’ll also have to attend placements at hospitals and other dental settings to learn all the skills you need to be a safe and competent dentist.
This means that it’s not possible to study all of dentistry online. Although the pandemic brought a temporary change to teaching styles, it’s likely that the majority of your dentistry course will take place in a physical setting.
How to get into dentistry with a low ATAR
You can still get into dentistry, even if your ATAR isn’t that high. You have two main options before you:
Check if you’re eligible for any special pathways or bonuses (such as for rural/remote and Indigenous students).
Do an undergraduate degree in a related subject with lower ATAR requirements and try for graduate entry dentistry.
Dental schools with pathways
The following universities have certain pathways that can result in you achieving additional points, this could compensate for a slightly lower ATAR. You need to check each university's requirements in detail and how to apply to make sure you don’t miss any deadlines.
Charles Sturt University
Charles Sturt has a range of pathways including:
Griffith University
The university has a rural priority access scheme for students living in RA 2-5. Students who have lived RA 2-5 for a minimum of five consecutive years or 10 cumulative years will have priority access to the course. You’ll need to apply for this via QTAC.
La Trobe
La Trobe has a range of pathways. If you’re eligible for more than one, the maximum possible adjustment you can get is 20.
One of the pathways at La Trobe is the Special Entry Access Scheme (SEAS). There are four categories for which you can be eligible for:
Personal information and location
Disadvantaged financial background
Disability or medical condition
Difficult circumstances
You’ll be able to find the details of all of the above on the SEAS site.
La Trobe also has a Rural and Regional Student Access Scheme (RRSAS). If you live in an RA 2 or 3 area, you’ll have 10 points added. For a postcode in RA 4, this will be 12.5 and 15 points for an area in RA 5.
La Trobe also has a priority access program for students going to certain schools.
University of Adelaide
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Pathway
Rural Background Entry Pathway
More information about entry pathways is available in their admissions guide.
University of Queensland
The University of Queensland has a rural access scheme. You need to have lived in an RA 2-5 postcode, for at least five consecutive years or 10 cumulative years. They also have an Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Admission Pathway. Click on the links for more details on eligibility and how to apply.
Graduate entry dentistry
You can apply to the following bachelor programs after completing a degree:
Charles Sturt University
If you're enrolled on a course at CSU and you have completed a minimum of four standard subjects (32 credit points) with a GPA above 5.5, you can apply for the 5-year Bachelor of Dental Science. If you don’t meet the criteria to apply as a current CSU student, you can apply as a regular domestic student or (if you’re eligible) as a rural or indigenous applicant.
Griffith University
If you are successful on the 3-year Bachelor of Dental Health Science, you’ll seamlessly be moved to the 2-year Master of Dentistry program, which will allow registration with the General Dental Council.
James Cook University
You can apply as a graduate to the 5-year Bachelor of Dental Surgery program. Your most recent GPA will be used to assess your application.
In 2025, a GPA of 5.75 on a 7 point scale was needed to be considered for an offer. This doesn't guarantee a place on the course however. If your course doesn't generate a GPA, you will be unable to apply.
University of Adelaide
You can apply with your GPA for the 5-year Bachelor of Dental Surgery. You need to have a minimum GPA of 5.0 to be eligible to apply. You’ll also need to meet the subject prerequisites which are as follows:
One subject chosen from:
Chemistry
Mathematical Methods
Specialist Mathematics
Physics
And one subject chosen from:
Biology
Geology
Chemistry
Physics
University of Otago
You can apply as a graduate for the 5-year Bachelor of Dental Surgery degree. You’ll be ranked based on a score calculated from the score you achieved in the first degree you took at university. There isn’t any preference given to the subject or degree qualification.
University of Melbourne
You can apply for the 4-year Doctor of Dental Surgery. You will need to have completed a bachelor's degree within 10 years of commencing your Doctor of Dental Surgery degree. You’ll need to take an admissions test, this will vary depending on where you are based, but if you’re in Australia it will be the GAMSAT.
You’ll be ranked based on your GPA and your admissions test score. You can find full details of requirements at Doctor of Dental Surgery: Entry requirements.
University of Sydney
You can apply for a 4-year Doctor of Dental Medicine degree. Your GPA and admissions test result will be used to select candidates. The admission test will vary depending on where you are based, but if you’re in Australia it will be the GAMSAT.
University of Western Australia
To study the 4-year Doctor of Dental Medicine, you’ll need a minimum GPA of 5.5 and a minimum overall GAMSAT score of 55 with no section score less than 50 for domestic applicants.
Dentistry scholarships
Most universities offer scholarships to help cover the cost of study. Check the websites of the dental schools you’re applying to, to see what scholarships you’re eligible for.
You can also check scholarship databases like:
There are also scholarship databases specifically for healthcare professionals:
There are also dentistry specific scholarships:
You can find lots more information on scholarships on the my health career page.
Can I study dentistry abroad in English?
Several Eastern European countries, including Georgia, Ukraine, Bulgaria, Armenia, and Romania, offer dental courses for foreigners. Studying abroad is becoming more and more popular, as the costs of living are lower and the competition less intense in these countries than in the UK. Tuition, too, is usually lower and starts from as little as $5500 per year.
Most of the above courses are taught in English and degrees from these countries are recognised internationally. Most of these countries also offer graduate entry dentistry courses. It’s likely that you’ll have to take a university-specific admissions test as part of their selection process, as there is no internationally accepted test.
Another option is to study dentistry in the UK. As the main language in the UK is English, you’ll have less trouble interacting with locals and settling in. However, tuition fees can be very expensive for international students: they range anywhere from $64,000 to $90,000 a year. Accommodation, living costs, and utilities can cost you over $100,000 over the five years.
What happens after graduating?
Once you’ve graduated, you’ll need to register with the Dental Board of Australia or the Dental Council of New Zealand. Once registered, you can work as a registered dentist. If you want to specialise, you’ll need to do further courses. These courses tend to be around three years but some may be longer and shorter depending on the specialty.
On this page
Studying Dentistry in Australia and New Zealand: A Complete Guide
Find out all you need to know about studying dentistry in ANZ, including different routes into dentistry, entry requirements, and tips for admission.

This article is written specifically for ANZ students.
Read the UK version here.
Table of contents
Dentistry has the power to transform lives.
That’s incredible in itself, but it’s also an in-demand profession with fantastic stability. The stumbling block for many is the high barrier to entry as university courses are extremely competitive and getting in takes total commitment.
Still interested? Read on to get a full breakdown of a career in dentistry.

Reasons to study dentistry


Is getting into dentistry competitive? What do I need and how can I improve my chances?
In short, yes. There are only 10 dental schools in Australia and New Zealand, with thousands of applicants eyeing a spot each year.
As a result, you need to think about your application holistically and prepare diligently to maximise your chances of success.
School grades
First, you will need strong academic credentials, such as an ATAR above 99 (for undergraduate courses) or a competitive GPA (for graduate courses). Prepare for your exams throughout the year to maintain high grades.
Admissions test
Second, you will need to perform well in an admissions test. Learn how these tests are run, find out the best resources to use, and start your preparation early.
If you’re applying as a school leaver or for undergraduate dentistry, it’s likely you’ll have to take the University Clinical Aptitude Test (UCAT ANZ). The UCAT ANZ is a two-hour, multiple choice, computer-based exam. It’s known for being extremely time pressured.
Improve your chances of succeeding in the UCAT by checking out the following resources:
Medify’s UCAT ANZ Online Course – 20,000+ questions, 25 unique full mock exams, 34 mini-mock exams, study notes and personalised performance feedback. You'll also get access to GAMSAT and Interviews courses.
If you’re applying as a graduate student, you may have to take the Graduate Medical Schools Admissions Test (GAMSAT). Find out more about the GAMSAT.
Interview
Third, most universities require an interview. Your interview will be in one of two formats:.
Semi-structured/panel
You’ll be interviewed by a panel of interviewers. Interviewers will ask you a series of questions and may also ask follow up questions. Semi-structured interviews have a less rigid format and are more likely to ask questions specific to you.
Multiple Mini Interview (MMI)
You’ll rotate around stations, and have a new interviewer and new interview question or task at each station. This format is much more structured as you’ll have a set amount of time at each station and all students will be asked the same questions.
Reflect on your motivations for dentistry, do readings around common dental topics and issues, and find out what dental school and dental career looks like.
Ask friends or family to help you out with mock interviews. This will help you become better at giving smooth and coherent answers. Interviews are always nerve racking so it’s important that you stay calm and make your answer relevant to the question.
Should I study dentistry or medicine?

How long does it take to become a dentist?
Becoming a dentist can take five or more years depending on the path you choose. A standard 5-year undergraduate degree in dentistry will allow you to practise once you’ve graduated.
Graduate entry degrees are four years long, but you need to already hold at least a bachelor's degree to take this path. This means that doing a graduate entry pathway would take you at least seven years, and if you chose to do a masters or any other degree after your bachelor’s it can take even longer.
What are dental schools looking for?
The Australian Dental Association suggests that dentistry is an ideal career for people that enjoy specific activities. This means dental schools are looking for students skilled in those areas as they will most likely be able to become good dentists.
These skills include:
Excellent communication
Ability to interact with a range of people
Strong interpersonal skills
Ability to work both in a team and independently
Broad scientific and medical knowledge
Manual dexterity
Hand eye coordination
Great spatial awareness
Leadership
Business management interest
Which subjects do I need to study dentistry?
Although there may be slight variations in subject prerequisites, generally you’ll be required to study Chemistry, Biology and English.
Subjects that are often mentioned include:
Chemistry
Biology
English
Physics
Math
Do I need work experience?
Although work experience isn't compulsory, having work experience could give you an advantage at interviews. It’s likely that you may be asked some questions about your understanding of what a career in dentistry entails.
Work experience in a dental setting will enable you to show that you have a realistic understanding of what a doctor does. It’ll help you prove your point rather than make empty claims.
The golden question for interviews: ‘Why do you want to study dentistry?'
This question is central to most interviews. Dentistry is challenging but also rewarding so interviewers want to make sure you’re doing dentistry for the right reasons.
Here are the do’s and don’ts to acing this question:
| Do | Don't | | --- | --- | | Talk about personal experience: If you had a personal experience that led you to want to study dentistry, discuss it and reflect on it. | Use clichés: Avoid phrases like 'I’ve always wanted to be a dentist' or 'I really enjoy helping people'. This may be the case, but it’s what everyone says. | | Talk about your work experience: Mention something you saw in your work experience that spurred you on to pursue dentistry. | Talk about salary: It may be an incentive for you, but you don't want to come across as money-minded. | | Take a balanced approach: Discuss the positives and negatives of a career in dentistry (so you won’t sound naive). | Disrespect other professions: Interviewers may ask you why not a dental nurse or dental hygienist? Speak about all other professions with respect, as without them you wouldn’t be able to do your job. | | Back up what you say: If you’re going to say you enjoy hands-on jobs, tell the interviewer about a hobby of yours that requires hands-on skills. | Talk about family members in dentistry: This can influence your decision, but it’s important to focus on your own reflection rather than someone else's experience. |
What’s the deadline for dental applications?
Dental application deadlines vary based on where you’re applying to. Different TACs have different deadlines.
The deadline is usually around the end of September but make sure you check each TAC’s site for information on deadlines.
Dental universities: Where can I study?
Charles Sturt University
1800 275 278
Griffith University
1800 677 728
James Cook University
enquiries@jcu.edu.au
1800 246 446
La Trobe
1300 135 045
University of Adelaide
1800 061 459
University of Melbourne
1800 136 352
University of Queensland
dentistry@enquire.uq.edu.au
07 3365 8022
University of Sydney
1800 793 864
University of Western Australia
future-students@uwa.edu.au
(+61 8) 6488 3939
Average cost of studying dentistry
In Australia, dental degrees cost around $300,000 for full-fee paying students and $55,000 for commonwealth supported place (CSP) students. You’ll also need to pay for the UCAT ($325) and some tertiary application centres have a fee for submitting applications ($55-$210).
On top of that, if you’re moving away from home, you’ll have accommodation and living costs to pay for. Accommodation and living costs can vary based on where you’ll be studying. For example, accommodation and living costs tend to be more expensive in Sydney compared to Adelaide. You can use this handy calculator to work out how much your living costs and accommodation will be.
If you’re doing a 5-year dental degree, it could end up costing up to $440,000. In New Zealand, tuition fee for dentistry is $16,187 per year for years 2–5.
Is there an option to study dentistry part-time?
There are no universities that currently offer part-time dentistry. However, you can study some postgraduate courses part-time.
Can I study dentistry online?
Dentistry requires a lot of patient contact. You’ll also have to attend placements at hospitals and other dental settings to learn all the skills you need to be a safe and competent dentist.
This means that it’s not possible to study all of dentistry online. Although the pandemic brought a temporary change to teaching styles, it’s likely that the majority of your dentistry course will take place in a physical setting.
How to get into dentistry with a low ATAR
You can still get into dentistry, even if your ATAR isn’t that high. You have two main options before you:
Check if you’re eligible for any special pathways or bonuses (such as for rural/remote and Indigenous students).
Do an undergraduate degree in a related subject with lower ATAR requirements and try for graduate entry dentistry.
Dental schools with pathways
The following universities have certain pathways that can result in you achieving additional points, this could compensate for a slightly lower ATAR. You need to check each university's requirements in detail and how to apply to make sure you don’t miss any deadlines.
Charles Sturt University
Charles Sturt has a range of pathways including:
Griffith University
The university has a rural priority access scheme for students living in RA 2-5. Students who have lived RA 2-5 for a minimum of five consecutive years or 10 cumulative years will have priority access to the course. You’ll need to apply for this via QTAC.
La Trobe
La Trobe has a range of pathways. If you’re eligible for more than one, the maximum possible adjustment you can get is 20.
One of the pathways at La Trobe is the Special Entry Access Scheme (SEAS). There are four categories for which you can be eligible for:
Personal information and location
Disadvantaged financial background
Disability or medical condition
Difficult circumstances
You’ll be able to find the details of all of the above on the SEAS site.
La Trobe also has a Rural and Regional Student Access Scheme (RRSAS). If you live in an RA 2 or 3 area, you’ll have 10 points added. For a postcode in RA 4, this will be 12.5 and 15 points for an area in RA 5.
La Trobe also has a priority access program for students going to certain schools.
University of Adelaide
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Pathway
Rural Background Entry Pathway
More information about entry pathways is available in their admissions guide.
University of Queensland
The University of Queensland has a rural access scheme. You need to have lived in an RA 2-5 postcode, for at least five consecutive years or 10 cumulative years. They also have an Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Admission Pathway. Click on the links for more details on eligibility and how to apply.
Graduate entry dentistry
You can apply to the following bachelor programs after completing a degree:
Charles Sturt University
If you're enrolled on a course at CSU and you have completed a minimum of four standard subjects (32 credit points) with a GPA above 5.5, you can apply for the 5-year Bachelor of Dental Science. If you don’t meet the criteria to apply as a current CSU student, you can apply as a regular domestic student or (if you’re eligible) as a rural or indigenous applicant.
Griffith University
If you are successful on the 3-year Bachelor of Dental Health Science, you’ll seamlessly be moved to the 2-year Master of Dentistry program, which will allow registration with the General Dental Council.
James Cook University
You can apply as a graduate to the 5-year Bachelor of Dental Surgery program. Your most recent GPA will be used to assess your application.
In 2025, a GPA of 5.75 on a 7 point scale was needed to be considered for an offer. This doesn't guarantee a place on the course however. If your course doesn't generate a GPA, you will be unable to apply.
University of Adelaide
You can apply with your GPA for the 5-year Bachelor of Dental Surgery. You need to have a minimum GPA of 5.0 to be eligible to apply. You’ll also need to meet the subject prerequisites which are as follows:
One subject chosen from:
Chemistry
Mathematical Methods
Specialist Mathematics
Physics
And one subject chosen from:
Biology
Geology
Chemistry
Physics
University of Otago
You can apply as a graduate for the 5-year Bachelor of Dental Surgery degree. You’ll be ranked based on a score calculated from the score you achieved in the first degree you took at university. There isn’t any preference given to the subject or degree qualification.
University of Melbourne
You can apply for the 4-year Doctor of Dental Surgery. You will need to have completed a bachelor's degree within 10 years of commencing your Doctor of Dental Surgery degree. You’ll need to take an admissions test, this will vary depending on where you are based, but if you’re in Australia it will be the GAMSAT.
You’ll be ranked based on your GPA and your admissions test score. You can find full details of requirements at Doctor of Dental Surgery: Entry requirements.
University of Sydney
You can apply for a 4-year Doctor of Dental Medicine degree. Your GPA and admissions test result will be used to select candidates. The admission test will vary depending on where you are based, but if you’re in Australia it will be the GAMSAT.
University of Western Australia
To study the 4-year Doctor of Dental Medicine, you’ll need a minimum GPA of 5.5 and a minimum overall GAMSAT score of 55 with no section score less than 50 for domestic applicants.
Dentistry scholarships
Most universities offer scholarships to help cover the cost of study. Check the websites of the dental schools you’re applying to, to see what scholarships you’re eligible for.
You can also check scholarship databases like:
There are also scholarship databases specifically for healthcare professionals:
There are also dentistry specific scholarships:
You can find lots more information on scholarships on the my health career page.
Can I study dentistry abroad in English?
Several Eastern European countries, including Georgia, Ukraine, Bulgaria, Armenia, and Romania, offer dental courses for foreigners. Studying abroad is becoming more and more popular, as the costs of living are lower and the competition less intense in these countries than in the UK. Tuition, too, is usually lower and starts from as little as $5500 per year.
Most of the above courses are taught in English and degrees from these countries are recognised internationally. Most of these countries also offer graduate entry dentistry courses. It’s likely that you’ll have to take a university-specific admissions test as part of their selection process, as there is no internationally accepted test.
Another option is to study dentistry in the UK. As the main language in the UK is English, you’ll have less trouble interacting with locals and settling in. However, tuition fees can be very expensive for international students: they range anywhere from $64,000 to $90,000 a year. Accommodation, living costs, and utilities can cost you over $100,000 over the five years.
What happens after graduating?
Once you’ve graduated, you’ll need to register with the Dental Board of Australia or the Dental Council of New Zealand. Once registered, you can work as a registered dentist. If you want to specialise, you’ll need to do further courses. These courses tend to be around three years but some may be longer and shorter depending on the specialty.
Studying Dentistry in Australia and New Zealand: A Complete Guide
Find out all you need to know about studying dentistry in ANZ, including different routes into dentistry, entry requirements, and tips for admission.

This article is written specifically for ANZ students.
Read the UK version here.
Table of contents
Dentistry has the power to transform lives.
That’s incredible in itself, but it’s also an in-demand profession with fantastic stability. The stumbling block for many is the high barrier to entry as university courses are extremely competitive and getting in takes total commitment.
Still interested? Read on to get a full breakdown of a career in dentistry.

Reasons to study dentistry


Is getting into dentistry competitive? What do I need and how can I improve my chances?
In short, yes. There are only 10 dental schools in Australia and New Zealand, with thousands of applicants eyeing a spot each year.
As a result, you need to think about your application holistically and prepare diligently to maximise your chances of success.
School grades
First, you will need strong academic credentials, such as an ATAR above 99 (for undergraduate courses) or a competitive GPA (for graduate courses). Prepare for your exams throughout the year to maintain high grades.
Admissions test
Second, you will need to perform well in an admissions test. Learn how these tests are run, find out the best resources to use, and start your preparation early.
If you’re applying as a school leaver or for undergraduate dentistry, it’s likely you’ll have to take the University Clinical Aptitude Test (UCAT ANZ). The UCAT ANZ is a two-hour, multiple choice, computer-based exam. It’s known for being extremely time pressured.
Improve your chances of succeeding in the UCAT by checking out the following resources:
Medify’s UCAT ANZ Online Course – 20,000+ questions, 25 unique full mock exams, 34 mini-mock exams, study notes and personalised performance feedback. You'll also get access to GAMSAT and Interviews courses.
If you’re applying as a graduate student, you may have to take the Graduate Medical Schools Admissions Test (GAMSAT). Find out more about the GAMSAT.
Interview
Third, most universities require an interview. Your interview will be in one of two formats:.
Semi-structured/panel
You’ll be interviewed by a panel of interviewers. Interviewers will ask you a series of questions and may also ask follow up questions. Semi-structured interviews have a less rigid format and are more likely to ask questions specific to you.
Multiple Mini Interview (MMI)
You’ll rotate around stations, and have a new interviewer and new interview question or task at each station. This format is much more structured as you’ll have a set amount of time at each station and all students will be asked the same questions.
Reflect on your motivations for dentistry, do readings around common dental topics and issues, and find out what dental school and dental career looks like.
Ask friends or family to help you out with mock interviews. This will help you become better at giving smooth and coherent answers. Interviews are always nerve racking so it’s important that you stay calm and make your answer relevant to the question.
Should I study dentistry or medicine?

How long does it take to become a dentist?
Becoming a dentist can take five or more years depending on the path you choose. A standard 5-year undergraduate degree in dentistry will allow you to practise once you’ve graduated.
Graduate entry degrees are four years long, but you need to already hold at least a bachelor's degree to take this path. This means that doing a graduate entry pathway would take you at least seven years, and if you chose to do a masters or any other degree after your bachelor’s it can take even longer.
What are dental schools looking for?
The Australian Dental Association suggests that dentistry is an ideal career for people that enjoy specific activities. This means dental schools are looking for students skilled in those areas as they will most likely be able to become good dentists.
These skills include:
Excellent communication
Ability to interact with a range of people
Strong interpersonal skills
Ability to work both in a team and independently
Broad scientific and medical knowledge
Manual dexterity
Hand eye coordination
Great spatial awareness
Leadership
Business management interest
Which subjects do I need to study dentistry?
Although there may be slight variations in subject prerequisites, generally you’ll be required to study Chemistry, Biology and English.
Subjects that are often mentioned include:
Chemistry
Biology
English
Physics
Math
Do I need work experience?
Although work experience isn't compulsory, having work experience could give you an advantage at interviews. It’s likely that you may be asked some questions about your understanding of what a career in dentistry entails.
Work experience in a dental setting will enable you to show that you have a realistic understanding of what a doctor does. It’ll help you prove your point rather than make empty claims.
The golden question for interviews: ‘Why do you want to study dentistry?'
This question is central to most interviews. Dentistry is challenging but also rewarding so interviewers want to make sure you’re doing dentistry for the right reasons.
Here are the do’s and don’ts to acing this question:
| Do | Don't | | --- | --- | | Talk about personal experience: If you had a personal experience that led you to want to study dentistry, discuss it and reflect on it. | Use clichés: Avoid phrases like 'I’ve always wanted to be a dentist' or 'I really enjoy helping people'. This may be the case, but it’s what everyone says. | | Talk about your work experience: Mention something you saw in your work experience that spurred you on to pursue dentistry. | Talk about salary: It may be an incentive for you, but you don't want to come across as money-minded. | | Take a balanced approach: Discuss the positives and negatives of a career in dentistry (so you won’t sound naive). | Disrespect other professions: Interviewers may ask you why not a dental nurse or dental hygienist? Speak about all other professions with respect, as without them you wouldn’t be able to do your job. | | Back up what you say: If you’re going to say you enjoy hands-on jobs, tell the interviewer about a hobby of yours that requires hands-on skills. | Talk about family members in dentistry: This can influence your decision, but it’s important to focus on your own reflection rather than someone else's experience. |
What’s the deadline for dental applications?
Dental application deadlines vary based on where you’re applying to. Different TACs have different deadlines.
The deadline is usually around the end of September but make sure you check each TAC’s site for information on deadlines.
Dental universities: Where can I study?
Charles Sturt University
1800 275 278
Griffith University
1800 677 728
James Cook University
enquiries@jcu.edu.au
1800 246 446
La Trobe
1300 135 045
University of Adelaide
1800 061 459
University of Melbourne
1800 136 352
University of Queensland
dentistry@enquire.uq.edu.au
07 3365 8022
University of Sydney
1800 793 864
University of Western Australia
future-students@uwa.edu.au
(+61 8) 6488 3939
Average cost of studying dentistry
In Australia, dental degrees cost around $300,000 for full-fee paying students and $55,000 for commonwealth supported place (CSP) students. You’ll also need to pay for the UCAT ($325) and some tertiary application centres have a fee for submitting applications ($55-$210).
On top of that, if you’re moving away from home, you’ll have accommodation and living costs to pay for. Accommodation and living costs can vary based on where you’ll be studying. For example, accommodation and living costs tend to be more expensive in Sydney compared to Adelaide. You can use this handy calculator to work out how much your living costs and accommodation will be.
If you’re doing a 5-year dental degree, it could end up costing up to $440,000. In New Zealand, tuition fee for dentistry is $16,187 per year for years 2–5.
Is there an option to study dentistry part-time?
There are no universities that currently offer part-time dentistry. However, you can study some postgraduate courses part-time.
Can I study dentistry online?
Dentistry requires a lot of patient contact. You’ll also have to attend placements at hospitals and other dental settings to learn all the skills you need to be a safe and competent dentist.
This means that it’s not possible to study all of dentistry online. Although the pandemic brought a temporary change to teaching styles, it’s likely that the majority of your dentistry course will take place in a physical setting.
How to get into dentistry with a low ATAR
You can still get into dentistry, even if your ATAR isn’t that high. You have two main options before you:
Check if you’re eligible for any special pathways or bonuses (such as for rural/remote and Indigenous students).
Do an undergraduate degree in a related subject with lower ATAR requirements and try for graduate entry dentistry.
Dental schools with pathways
The following universities have certain pathways that can result in you achieving additional points, this could compensate for a slightly lower ATAR. You need to check each university's requirements in detail and how to apply to make sure you don’t miss any deadlines.
Charles Sturt University
Charles Sturt has a range of pathways including:
Griffith University
The university has a rural priority access scheme for students living in RA 2-5. Students who have lived RA 2-5 for a minimum of five consecutive years or 10 cumulative years will have priority access to the course. You’ll need to apply for this via QTAC.
La Trobe
La Trobe has a range of pathways. If you’re eligible for more than one, the maximum possible adjustment you can get is 20.
One of the pathways at La Trobe is the Special Entry Access Scheme (SEAS). There are four categories for which you can be eligible for:
Personal information and location
Disadvantaged financial background
Disability or medical condition
Difficult circumstances
You’ll be able to find the details of all of the above on the SEAS site.
La Trobe also has a Rural and Regional Student Access Scheme (RRSAS). If you live in an RA 2 or 3 area, you’ll have 10 points added. For a postcode in RA 4, this will be 12.5 and 15 points for an area in RA 5.
La Trobe also has a priority access program for students going to certain schools.
University of Adelaide
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Pathway
Rural Background Entry Pathway
More information about entry pathways is available in their admissions guide.
University of Queensland
The University of Queensland has a rural access scheme. You need to have lived in an RA 2-5 postcode, for at least five consecutive years or 10 cumulative years. They also have an Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Admission Pathway. Click on the links for more details on eligibility and how to apply.
Graduate entry dentistry
You can apply to the following bachelor programs after completing a degree:
Charles Sturt University
If you're enrolled on a course at CSU and you have completed a minimum of four standard subjects (32 credit points) with a GPA above 5.5, you can apply for the 5-year Bachelor of Dental Science. If you don’t meet the criteria to apply as a current CSU student, you can apply as a regular domestic student or (if you’re eligible) as a rural or indigenous applicant.
Griffith University
If you are successful on the 3-year Bachelor of Dental Health Science, you’ll seamlessly be moved to the 2-year Master of Dentistry program, which will allow registration with the General Dental Council.
James Cook University
You can apply as a graduate to the 5-year Bachelor of Dental Surgery program. Your most recent GPA will be used to assess your application.
In 2025, a GPA of 5.75 on a 7 point scale was needed to be considered for an offer. This doesn't guarantee a place on the course however. If your course doesn't generate a GPA, you will be unable to apply.
University of Adelaide
You can apply with your GPA for the 5-year Bachelor of Dental Surgery. You need to have a minimum GPA of 5.0 to be eligible to apply. You’ll also need to meet the subject prerequisites which are as follows:
One subject chosen from:
Chemistry
Mathematical Methods
Specialist Mathematics
Physics
And one subject chosen from:
Biology
Geology
Chemistry
Physics
University of Otago
You can apply as a graduate for the 5-year Bachelor of Dental Surgery degree. You’ll be ranked based on a score calculated from the score you achieved in the first degree you took at university. There isn’t any preference given to the subject or degree qualification.
University of Melbourne
You can apply for the 4-year Doctor of Dental Surgery. You will need to have completed a bachelor's degree within 10 years of commencing your Doctor of Dental Surgery degree. You’ll need to take an admissions test, this will vary depending on where you are based, but if you’re in Australia it will be the GAMSAT.
You’ll be ranked based on your GPA and your admissions test score. You can find full details of requirements at Doctor of Dental Surgery: Entry requirements.
University of Sydney
You can apply for a 4-year Doctor of Dental Medicine degree. Your GPA and admissions test result will be used to select candidates. The admission test will vary depending on where you are based, but if you’re in Australia it will be the GAMSAT.
University of Western Australia
To study the 4-year Doctor of Dental Medicine, you’ll need a minimum GPA of 5.5 and a minimum overall GAMSAT score of 55 with no section score less than 50 for domestic applicants.
Dentistry scholarships
Most universities offer scholarships to help cover the cost of study. Check the websites of the dental schools you’re applying to, to see what scholarships you’re eligible for.
You can also check scholarship databases like:
There are also scholarship databases specifically for healthcare professionals:
There are also dentistry specific scholarships:
You can find lots more information on scholarships on the my health career page.
Can I study dentistry abroad in English?
Several Eastern European countries, including Georgia, Ukraine, Bulgaria, Armenia, and Romania, offer dental courses for foreigners. Studying abroad is becoming more and more popular, as the costs of living are lower and the competition less intense in these countries than in the UK. Tuition, too, is usually lower and starts from as little as $5500 per year.
Most of the above courses are taught in English and degrees from these countries are recognised internationally. Most of these countries also offer graduate entry dentistry courses. It’s likely that you’ll have to take a university-specific admissions test as part of their selection process, as there is no internationally accepted test.
Another option is to study dentistry in the UK. As the main language in the UK is English, you’ll have less trouble interacting with locals and settling in. However, tuition fees can be very expensive for international students: they range anywhere from $64,000 to $90,000 a year. Accommodation, living costs, and utilities can cost you over $100,000 over the five years.
What happens after graduating?
Once you’ve graduated, you’ll need to register with the Dental Board of Australia or the Dental Council of New Zealand. Once registered, you can work as a registered dentist. If you want to specialise, you’ll need to do further courses. These courses tend to be around three years but some may be longer and shorter depending on the specialty.
More like this

UCAT ANZ Can Be Used for Medical School Admission In The UK
Considering studying in the UK? You'll be glad to learn that you can use your UCAT ANZ score to apply to UK medical schools.

UCAT ANZ Can Be Used for Medical School Admission In The UK
Considering studying in the UK? You'll be glad to learn that you can use your UCAT ANZ score to apply to UK medical schools.

UCAT ANZ Can Be Used for Medical School Admission In The UK
Considering studying in the UK? You'll be glad to learn that you can use your UCAT ANZ score to apply to UK medical schools.

The Importance of Manual Dexterity in Medicine and Dentistry
Find out what manual dexterity is and why it is important for medical and dental school interviews. Learn how to improve your manual dexterity.

The Importance of Manual Dexterity in Medicine and Dentistry
Find out what manual dexterity is and why it is important for medical and dental school interviews. Learn how to improve your manual dexterity.

The Importance of Manual Dexterity in Medicine and Dentistry
Find out what manual dexterity is and why it is important for medical and dental school interviews. Learn how to improve your manual dexterity.

What is the UCAT ANZ? 40 Top Questions Answered
We answer the top 40 questions about the UCAT ANZ.

What is the UCAT ANZ? 40 Top Questions Answered
We answer the top 40 questions about the UCAT ANZ.

What is the UCAT ANZ? 40 Top Questions Answered
We answer the top 40 questions about the UCAT ANZ.
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·

Join the 2 in 3 ANZ applicants who use Medify
That’s 220,000 students since 2009
Resources
© Medify Ltd 2009-2026
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·

Join the 2 in 3 ANZ applicants who use Medify
That’s 220,000 students since 2009
Resources
© Medify Ltd 2009-2026
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·
Start your journey with Medify today ·

Join the 2 in 3 ANZ applicants who use Medify
That’s 220,000 students since 2009
Resources
© Medify Ltd 2009-2026