Medical and Dental School Interviews
Find out about the different types of medical and dental school interviews, the best ways to prepare, the types of questions you might be asked and more.
Updated 13 Feb 2025
Dreaming of that place in medical or dental school?
Interviews are your chance to make the right impression and show that you’ve thought this through.
The article is designed to get you started. To make sure you’re fully prepared, check out our UK Interviews Online Course, which provides everything you need to excel in your medical school interview. Prepare at your own pace with in-depth study notes, authentic example video responses from real students, and an extensive Knowledge Bank as part of your Medify subscription.
Types of interview
Understanding the types of interviews is key to being prepared
Medical schools have different ways of interviewing applicants. The most common are panel interviews and multiple mini-interviews (MMIs), though if you are applying to Oxford or Cambridge, you’ll have a completely different kind of interview.
How do panel interviews and MMIs compare?
How do you prepare for panel interviews?
Learn how to wait before providing an answer
Even though you don’t have time to prepare, you should take a few moments after you’ve been asked the question to quickly arrange your thoughts, so that you can give a clear answer rather than a jumbled answer. Asking for a moment can actually give a great impression.
Practise speaking to groups of people
It's important to create rapport with the whole panel of examiners. When you’re in social situations, practice making eye contact with the whole group and making sure everyone feels listened to.
How do you prepare for MMIs?
We go into greater detail in our MMI article, but as a broad overview, you can prepare by working on the following:
Time management
Train yourself with a strict time limit of about 7–8 minutes to answer questions and learn to respond to prompts adequately in this timeframe.
Simulating the structure of the interview
Since each station is like the start of a new interview, the structure takes some getting used to.
Simulate the interview by asking friends or family to ask you typical interview questions at separate stations. This can create some familiarity with the format, which will be a huge help on the day.
Oxford and Cambridge medical interview preparation
‘Oxbridge’ (Oxford and Cambridge) interviews are designed to see how you deal with unfamiliar questions. The interview format is similar to their teaching style and they want to see if you would thrive in this environment.
Be prepared for random topics designed to test your problem-solving skills. Explain your thought process to the interviewer.
An example of these kinds of questions:
'What is the concentration of water?'
'How would you weigh a mountain?'
'How is a city like a cell?'
You could also be presented with an X-ray or the results of an experiment to discuss. You don’t need to have an in-depth knowledge of X-ray images, but the interviewer will give you some hints and cues, which you should use when discussing your answer.
Take on board everything the interviewer tells you to increase your chances of giving a good answer.
Top preparation tips for Oxford and Cambridge interviews
Revise your A-level content/school curriculum
Make sure it’s fresh in your mind, as it can help you to answer questions.
Read beyond your curriculum
Your interviewer will ask you science-based questions, so the more you read, the more confident you’ll feel to answer their questions. Wider reading also shows that you have a passion for the subject.
Practise answering creative questions
These questions can be tough as they are unpredictable. Your mind may go blank at first, but with practice you can improve. Ask a friend or family member to fire unusual questions at you. You could also practise alone by looking up previous questions and quickly jotting down bullet points without preparation.
General interview preparation

Work out your strengths and weaknesses
Make a comprehensive list of your positive and negative attributes framed around a healthcare context. Be honest.
Don’t try the classic trick of presenting one of your strengths as a weakness by saying something like 'I’m a perfectionist' or 'I work too hard'. Interviewees can tell that you’re dodging the question and that you haven’t really done much self-reflection.
Don’t say anything that is a major red flag for medicine or dentistry like 'I struggle to communicate with people', or 'I don’t work well under pressure'.
Discuss how you’re planning on improving these weaknesses.
Read as much as you can
Here are 5 books to read before medical school interviews. Not much of a reader? Here's our top podcasts for medical students.
We also recommend reading these two essential guides:
Read articles on ethics and other relevant topics, so you’re as well informed as possible. The more topics you’re familiar with, the more you can talk about.
Stay up to date with current affairs
Find out what’s going on in the healthcare, biomedical and medical fields. When you read news articles on non-healthcare related issues, think about how it can impact the medical and dental fields.
Keep up-to-date while you’re on the go with the BBC news app. If anything in particular interests you then write it down along with where you found it. With this technique, you can mention where you found your information when discussing current affairs in your interview. This will make you sound much more credible.
That being said, only talk about news you’ve found through respectable sources. It’s probably not a good idea to talk about things you’ve found on Reddit or YouTube. Learn how to identify fake news.
Make a skills bank
It can be hard to think of ideas under pressure. Few of us can recall a time we showed resilience or leadership on the spot. So in preparation for this kind of question, make yourself a bank of examples to show when you used a certain skill and reflect on it.
Here’s an example of what your skills bank could look like:
Make a checklist of topics you need to read and research before your interview

Here's an example pre-interview checklist for medicine and/or dentistry:
Finishing my skills bank
Mastering knowledge of NHS values
Gathering important medical/ dental stories from the past, e.g. Dr Bawa Garba, Charlie Guard
Gaining sufficient knowledge of various bodies like the General Medical Council, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, British Medical Association, World Health Organization, General Dental Council, British Dental Association.
Mastering relevant knowledge of the NHS (how it works, challenges, patient journey through primary and secondary care)
Mastering ethics knowledge, particularly around:
4 pillars of ethics: autonomy, justice, beneficence, and non-maleficence
Euthanasia
Abortions
Refusal of treatment
Organ donation
Consent
Confidentiality
Capacity and Gillick competence
Only for medicine
Gaining sufficient knowledge of common conditions, particularly:
Diabetes
Obesity
Covid
Long Covid
Cancer
Heart disease
Reviewing hot topics (i.e., topics in the news, which can change year to year)
Only for dentistry
Units of dental activity
NHS price bands
NHS traffic light system
Sugar tax
Fluoridation of water
Private vs NHS dentistry
Barriers to oral health
Health conditions:
Gum disease
Periodontitis
Effect of lifestyle choices on oral health , e.g. smoking, excessive sugar consumption
Oral cancer
Amalgam and Composites
Crowns and root canal
Medical and dental school interview questions

Check out our free model interview answers (medicine/dentistry).
Here are some additional, commonly covered medical and dental school interview question types:
Extra-curricular activities
Know the specifics of the activities you listed in your application, including any organisational details. Interviewers also want to see how this experience relates to you becoming a good doctor or dentist.
Work experience
Know what you did, what you saw, who you shadowed, and what you learned. You may get asked about whether your work experience has changed your insight into medicine or dentistry, or what qualities you or your colleagues demonstrated.
Reference
Know your letter of reference inside and out so you can answer questions about it.
School-specific questions
Some schools will ask you why you chose them. Prepare answers for why you were attracted to that particular school. Was it the course structure, location, research, extra-curricular activities or something else entirely?
The medical or dental profession
You may be asked a question about anything topical or newsworthy. Examples include the NHS response to COVID-19 and the current state of the NHS. Interviewers may also ask for your opinion on the qualities of a good doctor. Take time to reflect on this.
Personal attributes
You may be asked to list examples of how you have demonstrated teamwork, communication skills or empathy.
Motivation and insight into the profession
Make sure you know why you want to be a medic or dentist. Avoid generic answers like 'I like helping others'. Make your reasons for doing medicine or dentistry personal to you. You also need to have an awareness of other roles within the medical and dental fields like nurses, physiotherapists, dental nurses and dental hygienists. You need to know how they are different from being a medic dentist.
Also, make sure you understand the challenges of being a doctor or dentist. Neither is a bed of roses and so interviewers want to know that you have a realistic understanding of what you are getting into.
Sarah, from Newcastle University, told us about her interview experience:
‘Before my interview, I was provided with an online news article about “locked-in syndrome” and was required to read around the topic and to consider the ethical arguments at play in the issue of assisted suicide.
'I extensively researched the issues mentioned in the article online and even watched a French movie about the condition. This was to gain better insight into the experience of living with such a debilitating condition from a patient’s perspective.
'This then allowed me to consider both sides of the argument and apply it in the context of the article during my interview.'
Commonly asked interview questions for medicine
'Why do you want to be a doctor?'
'Why not a nurse or a physiotherapist?'
'Why this medical school?'
'Why is teamwork important in medicine?'
'Describe a time you displayed good communication skills'
'What makes a good doctor?'
'Can you tell me about a patient condition that caught your interest during your work experience or volunteering?'
'What do you know about the city this medical school is based in?'
'How do you deal with stress?'
Commonly asked interview questions for dentistry
'Why do you want to pursue dentistry?'
'What qualities should a dentist have?'
'Why this dental school?'
'What are some recent advances in dentistry?'
'Why do you want to study dentistry rather than medicine?'
Medify's UK Interviews Online Course contains over 150 common questions with model answers to help you improve your performance and find your own style.
Need inspiration for how to get started? Learn about Samar who got into Dentistry at Manchester on her second attempt.
Prepare with STARR to ace your interview
How you structure you answer varies depending on the question, but one useful approach is the STARR technique. This helps to demonstrate skills or qualities in a similar way that you would demonstrate them in a job interview.
STARR stands for:
Situation
Describe the situation you encountered which relates to a quality:
'I was helping at the reception of a GP practice when a lady who didn't speak very much English came to the counter. She wanted to know how to get the flu jab, but she was struggling to understand what was being said to her.'
Task
Describe the actions required:
'I needed to explain to the lady how to get a flu jab and help her book an appointment and make sure she understood.'
Action
Describe what actually happened and how you responded:
'I explained everything slowly, using simple language and avoiding figurative expressions to reduce the likelihood of miscommunication. I waited for the lady to understand what I had just said, before moving on.'
Result
What were the outcomes of the situation and was the issue resolved?
'The lady was able to book her flu jab and understood all the information.'
Reflection
What did you learn from the experience?
Ethical questions
You may encounter a general ethical question. The General Medical Council provides ethical guidance for medics. These are virtually identical to ethics for dentists and so are worth revising no matter what you plan to study.
When you are asked an ethics question, follow a three-step process.
1. You’ll first want to identify what ethical issues are involved. The first thing you will want to discuss is which pillar(s) of medical ethics is/are at stake.
There are 4 pillars in medical ethics:
Autonomy
A patient has a right to choose whether or not they want a certain treatment. Doctors and dentists have to respect that decision.
Beneficence
This is about having the best interests of a patient in mind, which means only doing things that will benefit them.
Non-Maleficence
This is about making sure no harm comes to a patient.
Justice
As a doctor or a dentist, you must treat everyone fairly and equally.
You could also briefly mention anything topical that you’ve read.
2. You’ll then want to discuss who is involved. This is an opportunity to show your empathy by considering who will be affected by your decision and how.
3. Finally, you want to discuss and weigh options. Explain potential courses of action and the advantages, disadvantages and implications of each.
An example ethical question: 'Should the fluoridation of water be allowed?'
First and foremost, if you don’t already know what ‘fluoridation of water’ means, ask the interviewer(s). Then once they’ve explained it to you:
Stay focused on the question and don’t digress.
Give a balanced answer by weighing up the positives and the negatives.
Try to link in any news articles or studies you may have read.
In the end, give your opinion. Don’t stay undecided as it can come across to interviewers that you lack decision-making skills.
Here's some examples of positives:
Maintains the dental health of the public
Reduces cost of dental problems for NHS
Fluoride is commonly present in groundwater and oceans anyway
Here's some examples of negatives:
Takes away the autonomy of the public
Poses questions regarding to what extent other people can choose for us (should sugar be banned? Should tanning salons be banned?)
There are studies that suggest that fluoridation can cause bone problems and even cancer, which can cause fear in the population and lead to distrust in governments
What does a good or bad interview answer look like?

It can be hard to understand what kind of answer interviewers are looking for. Here's an example of good and bad answers.
The interviewer asks: 'One of your fellow students on your medical course regularly misses lectures and stays in her room a lot. What would you be concerned about? What would you do?'
Bad answer
'I’d ask her why she’s not coming to lessons and explain that she risked not learning anything and not becoming a good doctor. I’d warn her that if she didn’t come to the next lesson, I’d contact the teachers and get them to make her come.'
This isn’t a good answer. The student isn’t being considerate about the reasons why she may not want to come. The student is rash in their decision-making process.
Good answer
'Well, there are a lot of reasons why somebody may be missing lessons and staying in their room a lot, they may be struggling with their mental health, or with the course content. It’s even possible they have something going on at home or haven’t been feeling well lately.
'My main concern would be the well-being of this student. Along with that, I’d be concerned about the fact that missing lessons will create gaps in her knowledge. She’s missing out on information that could aid her as a doctor and so it may affect her ability to perform in the future and consequently affect patient safety negatively.
'In this situation, I would go and meet her and just have a casual conversation. I wouldn’t confront her about this straight away but let her get friendly with me and comfortable speaking to me.
'I would start off by indirectly asking her how her classes are going. If she’s avoided the topic, then I would be more direct, and say:
‘I haven’t seen you in lessons for a while. Is everything okay?’
'I would listen to her patiently and wait for her to finish. If it was something I could help with then I would do my best to help her. If it was something beyond my control I would encourage her to seek help and support, using the mechanisms in place at the university.
'Throughout my conversation, I’d emphasise that I was there to listen to her and help her. I would also offer to help her catch up on any of the classes she’s missed so that any gaps in her knowledge would be filled.
'So my overall approach would be empathetic, by listening to her circumstances and guiding her to get the support that she needs.'
This is a good answer. The student takes a thoughtful approach to the situation and appreciates the need to establish more information. The student also expands much more on their answer and is sensitive and compassionate.
Interview FAQ

1. What qualities are medical and dental schools looking for?
Medical and dental schools are both training doctors and dentists to join the NHS workforce, so medical schools and dental schools will look for a lot of the same things. In the UK, both types of schools will want students who can live up to the NHS values:
Working together for patients
Respect and dignity
Commitment to quality of care
Compassion
Improving lives
Everyone counts
The Medical Schools Council have created a list of core values and attributes they believe you should have if you want to study medicine:

These are the skills and attributes of an ideal candidate for dentistry as described by the Dental Schools Council:
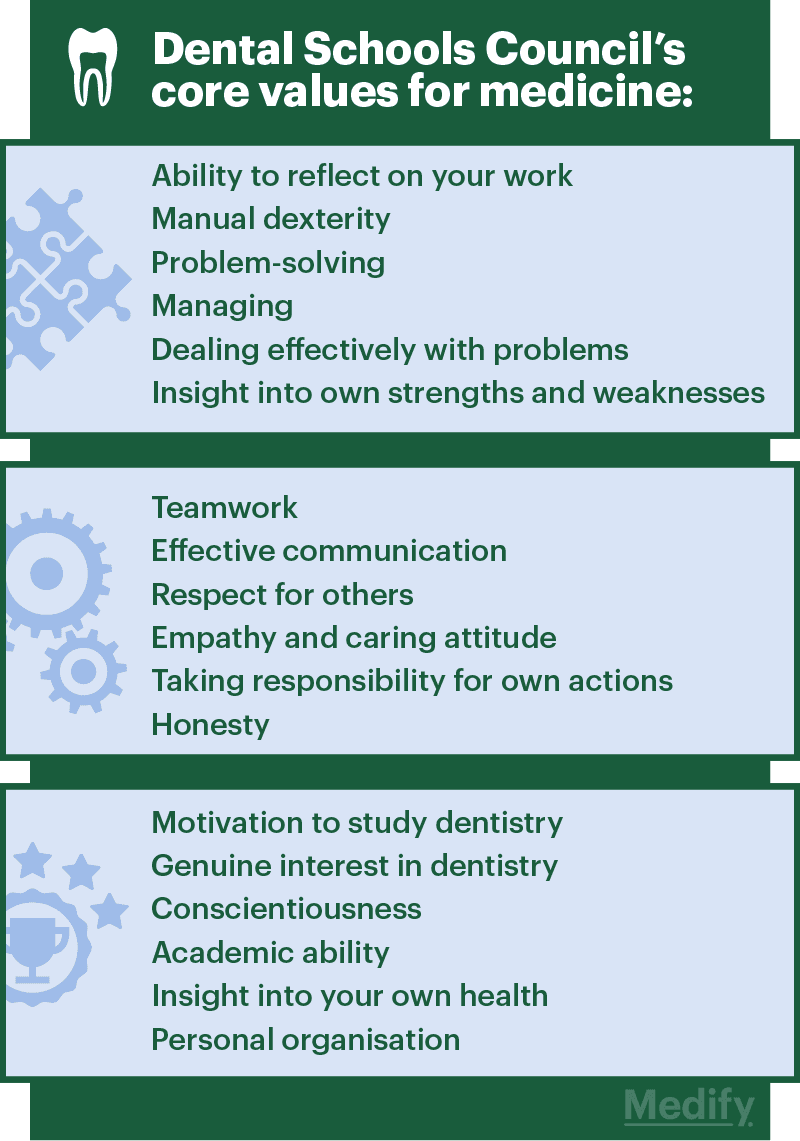
As you can see, the qualities required are very similar. The biggest difference is that dental schools also look for manual dexterity. The role of a dentist is very hands-on, so it’s important to have steady hands.
Find out more about manual dexterity.
2. Where can I find more information about interviews?
Since each medical and dental school has their unique style of interviews, you do not want to discover any nasty surprises on the day.
Read your interview invitation letter for instructions and any details of interview structure. For instance, the letter may tell you how many interviews to expect, where they are held and who will interview you
The official school website and admissions office will have useful information regarding the format of a school’s interview process, including the length of the interview and what type of questions they may ask
Use open days to ask current students about what interviewers have previously asked
Online forums are a useful source of information
Use all information with caution, as questions do change. It is worth noting that students at certain universities may not be allowed to disclose what they got asked and you may face consequences if you are found to be seeking these questions
Phoebe, from Swansea University, told us about her experience:
‘I had one awful interview during my first application, then four really enjoyable interviews on my re-application which were followed by four offers. If the interview goes badly, don’t give up; sometimes it just doesn’t go as planned for whatever reason. It may seem tricky because they are trying to challenge you, or it may be because that medical school isn’t really suited to you and your personality or learning style. Generally, the interviewers want to get the very best out of you and aren’t there to trip you up or make you feel uncomfortable.’
3. Do all medical and dental schools require an interview?
It’s highly unlikely that any student would receive an offer without an interview. Many universities explicitly state that they will not do this and even those who don’t state it explicitly almost always adhere to the same policy.
4. How likely am I to receive an interview?
Your likelihood for interviews hinges on a range of factors including:
Academics (A-levels and GCSEs or equivalent)
Personal statement
Generally, having a strong UCAT score and good academics will put you in a good position to receive an interview. The way universities select for an interview will vary between schools, so don’t worry if you feel like one part of your application is weaker than the other, as some medical and dental schools may not use that part as much.
5. How do I make a good first impression?
Interviewers are trained not to have any bias based on gender, race, age or religion, so you can fully take that out of the equation.
To make a good impression when you enter the room, make sure you smile - a genuine one. Big fake smiles are off-putting!
Greet all interviewers in the room politely. It's important to bear in mind that not all interviewers will want to shake hands, so you should use your own judgment for each interview and be aware of social distancing, where appropriate.
With MMIs you’ll have a different interviewer for each station and therefore a new opportunity to make a good impression each time. Don’t worry if your interaction with one of the interviewers was slightly awkward.
6. What should I wear to medical school interviews?

You should dress smartly for your interview in order to make a good first impression. Interviewers need to be able to visualise you working as a doctor.
It is best to wear a suit and tie, a dress or a shirt and skirt. Don’t wear bold shirts or overly patterned clothes. Instead, choose basic patterns and colours. Dress shoes, heels or flats are all appropriate footwear.
7. What if I feel nervous on the day?
It’s perfectly normal to feel nervous on the interview day. Your interviews are an important part of your medical school applications and that can put a lot of pressure on you. Here are some tips to help you feel less anxious for your interview:
Get there nice and early
Make sure you’ve had lots of practice
Remember why you’re doing this
Remember, interviewers don’t want you to fail
Try some of these mindfulness tricks
Visualise the best
Prepare for the worst
Plan something nice to do after your interview
Be yourself
Silence is okay
8. Should I memorise answers?
Absolutely not!
Most interviewers you’ll encounter will have been doing their job for many years and can tell when someone is just regurgitating an answer they’ve learned by heart. Interviewers want to know your thoughts, not how good your memory skills are.
Instead, use notes when you’re preparing to help you recall the gist of what you want to say. For example, for ‘Tell me about a time you worked in a team’, you might simply jot down the following:
School hockey team
Was team leader
Good listener
Had to communicate well
Motivate others
As we mentioned at the outset, this overview is meant to properly gear up for your interview preparation, and if you work through it carefully, it will get you off to a really great start.
If you really want to take your interviews skills to the next level, however, make sure you check out Medify's UK Interviews Online Course, which offers much more in-depth and detailed guidance on interview formats, what interviewers are looking for, how to prepare, how to conduct yourself and how to spin your unique circumstances if you’re a graduate or international applicant, along with many more possible interview topics and strategies for giving outstanding answers.
9. What if I’m late for my interview?
Try your absolute best to not be late. Maybe set out an hour early in case you run into any traffic, or you could even stay overnight at a hotel near the university. Use a digital map to make sure you have a good idea of the route before you set off.
If you are still going to be late, call up the university as soon as you can to inform them. Make sure you apologise and also explain why you’re late. Be prepared to face the consequences, as some universities will be prepared to wait while others may not.
10. How long are interviews?
The length of interviews can vary from university to university. It can last anywhere from 20 minutes to 2 hours. Universities will give details on how long the interview will be in your interview invite. It’s important to bear in mind that you won’t be talking for the whole of the time mentioned in your invite, which, in the case of MMIs, also accounts for the time spent moving from station to station. Some universities also give a tour of their facilities on the day.
12. Will I be asked about my personal statement?
Some interviewers will discuss your personal statement in the interview. This means that you should know your personal statement very well.
It also means that it’s crucial to be honest when writing it. If you're found to be dishonest in your personal statement, it can be really hard to recover during an interview.
The personal statement is changing to a series of free text questions for 2026 entry onwards.
13. Will interviews be in-person or online?
For 2025 entry, most medical and dental school interviews will be face-to-face, however there are a small number of medical and dental schools carrying out online interviews. You can check the lists below for more information.
It’s important to remember that whether they’re face-to-face or online, your preparation for interviews should generally be the same.
Medical school interview information
Undergraduate entry
Cardiff: MMI including a verbal interview and a written paper
Southampton: Selection day with a panel interview and group task
Graduate entry
Cardiff: MMI including a verbal interview and a written paper
Newcastle: MMI (home students), panel interviews (international)
Nottingham: A mix of MMI and panel interviews (may be face-to-face or online)
Southampton: Selection day with a panel interview and group task
Worcester: Two panel interviews plus CASPer (equally weighted)




